Insulin Resistance-What You Need to Know
Insulin resistance is when cells in your muscles, fat, and liver don’t answer well to insulin, a chemical made by your pancreas that deals with your blood glucose (glucose). Here and there, Insulin resistance is a momentary condition. However, whenever left untreated for quite a while, it could transform into diabetes.
Your body’s principal wellspring of fuel is glucose, which it gets by separating the food you eat. When glucose enters your circulation system, insulin assists it with getting into your cells, where it’s either utilized or put away for some other time. That flags your pancreas to quit making insulin.
In any case, assuming you have insulin obstruction, this cycle doesn’t function admirably. Your cells aren’t giving glucose access when insulin “inquires” them to. Therefore, increasingly more blood glucose stacks up in your circulation system. Also, your pancreas continues to make insulin.
For some time, your pancreas might have the option to make such an excess of additional insulin that your cells open up and allow in glucose how they should. That will keep your glucose inside a typical reach. Yet, over the long haul, your cells might turn out to be more insulin and your blood glucose levels could continue to rise.
Insulin resistance vs. diabetes
Insulin opposition and diabetes are connected yet not the equivalent.
In the event that you have insulin obstruction, your glucose is still inside an ordinary reach.
Prediabetes as a rule ends up peopling who have some insulin obstruction. Your glucose is higher than ordinary, yet at the same time not sufficiently high for diabetes.
Insulin opposition and prediabetes can both lead to type 2 diabetes. Such a lot of glucose stays in your circulation system, you will require prescription to treat it.
Insulin Resistance Symptoms
ou can’t perceive that you have insulin opposition by how you feel. You’ll have to get a blood test that checks your glucose levels.
In like manner, you won’t be aware assuming you have the majority of different circumstances that are essential for insulin obstruction disorder (hypertension, low “great” cholesterol levels, and high fatty substances) without seeing your PCP.
A few indications of insulin obstruction include:
- A waistline north of 40 crawls in men and 35 creeps in ladies
- Pulse readings of 130/80 or higher
- A fasting glucose level north of 100 milligrams for every deciliter (mg/dL)
- A fasting fatty oil level more than 150 mg/dL
- An HDL cholesterol level under 40 mg/dL in men and 50 mg/dL in ladies
- Skin labels
- Patches of dull, smooth skin under your arms or on your neck (acanthosis nigricans)
- Harm to little veins in the backs of your eyes, which can prompt a condition called retinopathy
What Causes Insulin Resistance?
Experts still don’t fully understand what causes insulin resistance and prediabetes.
- obesity: Particularly around the abdomen, and particularly instinctive fat, which is fat around the organs
- Actual inertia: Active work assists the body with turning out to be more delicate to insulin and fabricating muscle that can ingest blood glucose
- Diet: An eating regimen high in carbs, immersed fats, and profoundly handled food sources
- Family ancestry: A family background of type 2 diabetes
- Mature: Bound to happen after 45
- Race: Bound to happen in Dark, Hispanic, or Local American individuals
- Medical issues, For example, hypertension, unusual cholesterol levels, coronary illness, nonalcoholic greasy liver sickness, and polycystic ovary
- disorder
- Meds: Like steroids, some pulse meds, certain HIV medicines, and a few mental prescriptions
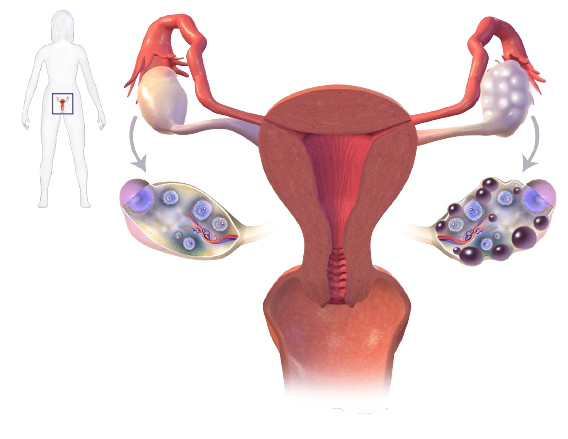
Insulin resistance and PCOS
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) affects up to 15% of the world’s population classified as female (AFAB). This is one of the most common causes of infertility.
If you have PCOS, you have an excess of a chemical called androgen. This may make it difficult for you to conceive. It also causes various side effects such as acne on the skin and hair. Most people with PCOS are insulin resistant.
The connection between insulin resistance and PCOS is unclear but is being investigated. Your family may suffer because you develop PCOS if your mother or sister has it, or type 2 diabetes. Obesity may also be a factor.
Insulin Resistance Diagnosis
A healthcare provider can detect insulin resistance with a blood test that measures fasting glucose. The test involves a fingerstick or venous blood sample and usually requires an 8-hour fast before the test. A fasting glucose level greater than 100 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) indicates insulin resistance.
The specialist may also obtain information about side effects, medical history, weight and pulse. Other symptoms of insulin resistance include:
- High glucose levels
- Products with a lot of fat
- High LDL (terrible) cholesterol.
- Low HDL (high) cholesterol.
- The wrist has more than 40 holes in men and 35 in women.
- Blood pressure reading is 130/80 or higher.
- skin symptoms
- Acanthosis nigricans are deep, tender areas of skin in the armpits or neck.
- Retinopathy, which affects the small blood vessels in the back of the eye.
How Insulin Resistance Progresses to Type 2 Diabetes
Insulin opposition is remembered to go before type 2 diabetes (T2D) by 10 to 15 years. Insulin opposition happens when cells in the body experience issues answering insulin, a chemical that assists cells with retaining glucose from food. As insulin obstruction declines, the pancreas delivers more insulin to redress, however the cells ultimately quit answering. At the point when the pancreas can’t keep up, glucose levels rise, which can prompt prediabetes or T2D.
Thus, insulin resistance can develop in T2DM:
- Insulin resistance
When the body consumes excess calories, insulin-resistant tissues such as skeletal muscle have difficulty maintaining glucose. - Hyperinsulinemia
The body needs more insulin to deliver glucose to insulin-resistant tissues, which can lead to hyperinsulinemia. - Beta cell weakness in the pancreas
Over time, the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas can break down and become less powerful. - Hyperglycemia
When the pancreas cannot deliver enough insulin to overcome the blockage, blood sugar levels rise, leading to hypoglycemia.